
If there’s anything we know for sure, it’s that your body goes through a wide variety of changes throughout pregnancy. These changes are normal and expected throughout every week of pregnancy. However, it’s important to make sure you’re getting all the vitamins and minerals you need to support a changing body and a growing baby. DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) and other omega-3 fatty acids directly contribute to healthy growth and development. DHA and EPA are the most important omega-3s. They are critical for a baby’s brain and eye development and have been shown to reduce the risk of gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, and preterm birth.
DHA is short for docosahexaenoic acid, a long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid.
It is a powerful omega-3 fatty acid required for a baby’s brain development. It plays a critical role in every cell of the body, especially for a growing baby. It is one of the most important nutrients that pregnant people need to consume during pregnancy.
Keep reading to discover why DHA is beneficial during pregnancy and how to get more DHA into your diet.

DHA and Pregnancy
Studies show that pregnant women should consume at least 300 milligrams (mg) of DHA daily to help promote a healthy pregnancy. However, up to 600 mg or more per day may be beneficial. DHA is essential during pregnancy because it is the primary structural component of the human brain, eyes, and skin.
It plays a big role in the growth and development of the baby’s nervous and immune systems. It is known to help prevent preterm labor and reduce inflammation. Maintaining good DHA status in late pregnancy, especially 34 weeks and on, is one of the best ways to support your baby’s final growth surge.
During the third trimester, the baby’s brain undergoes a significant growth spurt, accumulating DHA at a rapid pace to support cognitive and visual development. This is why maternal DHA levels are especially important now—your intake directly influences how much DHA is available to your baby. Maintaining good DHA status in late pregnancy, especially 34 weeks and on, is one of the best ways to support your baby’s final growth surge.
Food sources of DHA include fatty fish like salmon, sardines, and anchovies, but many pregnant women don’t consume fish regularly. In these cases, a high-quality, purified fish oil or algae oil supplement can help meet daily needs. If you’re vegetarian or vegan, algae oil is a plant-based DHA source that’s safe and effective. Getting enough DHA is a simple but powerful step to support both your health and your baby’s long-term development.
DHA And Pregnancy Benefits
Helps Prevent Preterm Labor
Research shows that consuming omega-3 fatty acids like DHA while pregnant greatly reduces the chances of preterm birth or early delivery. A premature delivery could be dangerous and result in a prolonged hospital stay. Getting at least 300 mg/day of DHA can help ensure a healthy and full-term pregnancy. This includes managing blood pressure and overall health.
Proper Blood Vessel Health
DHA also supports proper blood vessel function and may reduce the risk of pregnancy complications like preeclampsia. In addition to helping extend gestation to full term, DHA modulates the body’s inflammatory response, which is essential for maintaining a stable environment for fetal development. Prioritizing DHA is one of the most evidence-based steps in the third trimester! Consume foods like salmon, sardines, and herring every week!
Supports Baby’s Brain, Nervous System, and Eye Development
DHA is an essential building block for your baby’s brain, eye, and nervous system development. DHA is utilized on the cellular level to help promote healthy growth and the development of new cells that eventually turn into organs. It is important to consume DHA throughout your whole pregnancy, but DHA is particularly important in the third trimester when your baby’s brain is growing rapidly!
Helps Promote a Healthy Birth Weight
DHA is important because it directly contributes to your baby’s growth and weight at birth. A healthy birth weight reduces the risk of complications during and after birth. Your baby stores DHA consumed during pregnancy and continues to use it to maintain healthy growth and development until two years of age. In combination with other vitamins and a nutritious diet, DHA can help promote proper growth and development of your baby resulting in a healthy weight at birth and in the first few years.

Good Sources Of DHA During Pregnancy
Cold-Water Fish
The best source of DHA can be found in high-quality, cold-water, fatty fish like salmon, anchovies, sardines, and herring. There’s a good chance you’re already eating some of these fish regularly since they are generally recognized as a healthy food choice and one of the many foods that promote fertility. These fatty fish are high in DHA and other nutrients and low in mercury. You can get the required amount of DHA by consuming 8-12 ounces of fish per week. To help choose which fish are best to consume during pregnancy, check out this chart from the FDA.
Shellfish
Seafood is the best source of direct DHA, and shellfish falls into that category. I recommend including any type of low-mercury seafood you like in your prenatal diet. Shellfish should be cooked well to enjoy during pregnancy since raw options pose a higher food safety risk. Options such as scallops, lobster, shrimp, and crab are great for getting more DHA during pregnancy.
Pastured-Eggs
Pasture-raised or omega-3 enriched eggs can also provide DHA to you and your baby. Consuming just these products won’t be able to meet your daily requirement for DHA, but it can certainly help increase your DHA levels. In addition to DHA, eggs provide many other important nutrients during pregnancy, like choline, vitamin D, and selenium. When eating eggs, be sure to include the yolk – that’s where all the DHA and choline are located!
Walnuts and Chia Seeds
Nuts and seeds are one of many great snack ideas for pregnant women, and many are high in healthy fats like omega-3 fatty acids. It is important to note that nuts and seeds are a good source of omega-3 ALA (alpha-linolenic acid), not DHA. ALA has to be converted to DHA, and this is done so at a limited rate.
This means you cannot meet your DHA needs by eating nuts and seeds alone. However, including more walnuts, chia seeds, flaxseed, and pumpkin seeds in your diet, provides tons of benefits for pregnancy. These nuts and seeds are great salad toppings and the perfect ingredients for a healthy trail mix.

Supplements
Prenatal vitamins or a specific omega-3 supplement can be a great way to meet your DHA needs, especially if you don’t consume a lot of fatty fish. While some prenatal vitamins contain a partial or full daily dose of DHA, some do not contain any at all. Prenatal vitamins also contain other essential vitamins and minerals that are good to consume during pregnancy.
Make sure your omega-3 supplement is not made from flaxseed oil, as we mentioned above, this will not be sufficient to meet your DHA needs. And always be sure to check with your health care team before starting any new prenatal supplements. To learn more about omega-3 supplements and to find one that works for you, join The Prenatal Nutrition Library.

Can You Have Too Much DHA When Pregnant?
While it is possible to have too much DHA during pregnancy, it’s not a common concern for most people following typical supplement or dietary guidelines. Of course, the answer isn’t crystal clear, but at minimum, you should consume or supplement 300 mg of DHA daily. Evidence suggests that DHA at higher levels is generally safe; it’s best to stay under 1000 mg/day unless advised by your doctor.
It is suggested that DHA come from food first, and then fish oil supplements. If you do not eat fish at all or do not eat fish regularly (more than once per week), it’s likely you DO need to supplement DHA. Supplementation is likely needed if you don’t eat fatty fish 2–3 times weekly. Look for a third-party-tested supplement (discount code: RYANN) that includes both DHA and EPA. Always talk to your healthcare provider before starting high-dose DHA or fish oil supplements.
DHA During Pregnancy
DHA is essential during pregnancy because it directly contributes to your baby’s overall growth and development, including their brain. Although DHA is important throughout the entire pregnancy, you should try to up your intake even more during the third trimester. Remember, you need to consume direct sources of DHA as our body doesn’t make it and can only convert a small amount from foods you eat that contain ALA.
Always remember to stick to safe seafood during pregnancy and avoid fish high in mercury. If you have any additional questions about DHA, feel free to ask in the comments below! And for more information about all things prenatal health and pregnancy, join The Prenatal Nutrition Library!
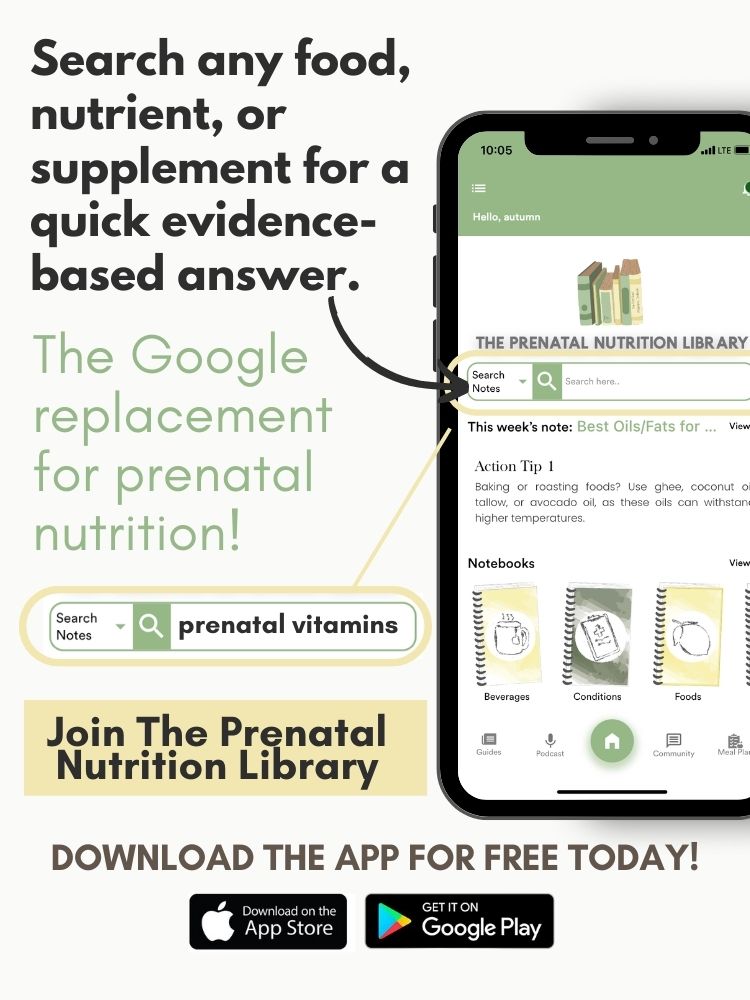
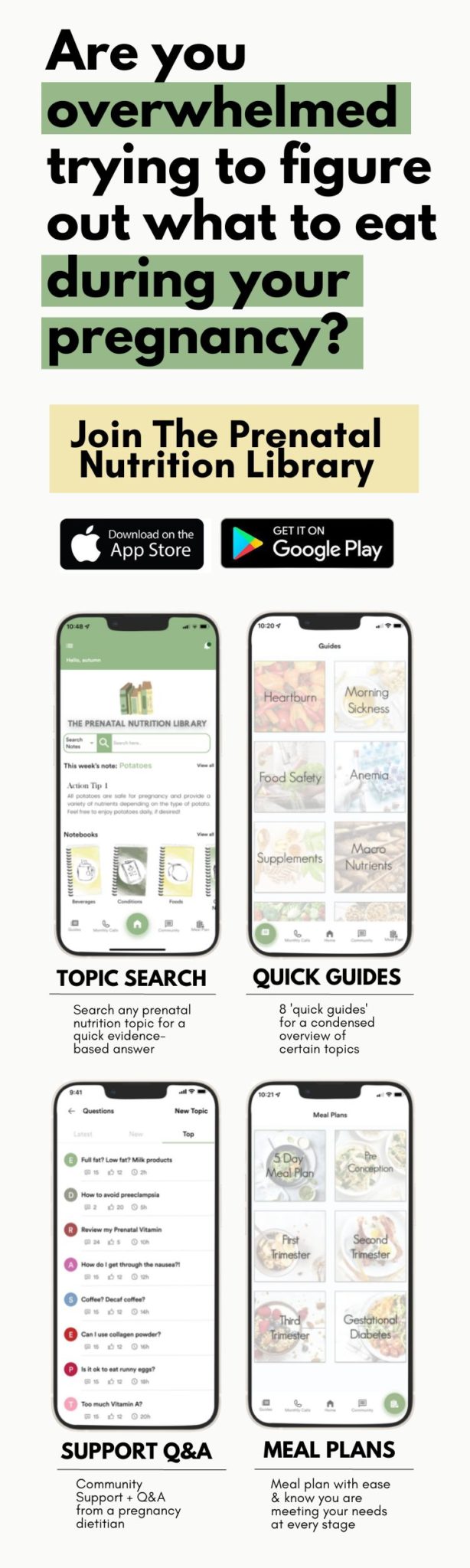
Don’t forget, you can also download our app for free on the App Store for easier access to tons of prenatal nutrition content.










33 weeks pregnant here and just realizing that my prenatal vitamin doesn’t inude DHA. I try to eat fish every week. But I don’t eat enough. Is it too late to start DHA supplement?