Preeclampsia, or high blood pressure during pregnancy, is a potentially dangerous complication of pregnancy. It’s defined by high blood pressure and, commonly, excess protein in the urine. It typically develops after 20 weeks of pregnancy or within 48 hours of delivery. It affects 5-8% of pregnancies and is one of the leading pregnancy complications worldwide. The exact cause of preeclampsia is unknown. However, risk factors include first pregnancies, multiple gestation, obesity, chronic hypertension, and gestational diabetes.
Elevated blood pressure and excess protein in the urine are key indicators of preeclampsia. When blood pressure reaches 140/90 mg/dl or higher on two occasions at least 6 hours apart after 20 weeks of gestation, a diagnosis of preeclampsia is made. Left untreated, the condition can progress to eclampsia, defined as preeclampsia with new-onset seizures unrelated to other cerebral conditions. Eclampsia is a medical emergency requiring prompt magnesium sulfate therapy and close monitoring to prevent further serious complications.
Depending on the severity of symptoms, preeclampsia can usually be managed on an outpatient basis with careful monitoring. In some circumstances, it could require hospitalization and medical treatment. Nutrition and lifestyle interventions can help control blood pressure during pregnancy. Magnesium sulfate therapy may be recommended in severe cases of preeclampsia.
This post will focus specifically on how magnesium can benefit women experiencing preeclampsia during pregnancy. I will discuss evidence on magnesium’s potential role in blood pressure regulation. As well as some information on what to expect if prescribed magnesium sulfate therapy for severe cases of preeclampsia.
Magnesium For Preeclampsia
Magnesium is a mineral that plays many vital roles in the body. It is involved in over 300 enzymatic reactions related to energy production, bone health, muscle and nerve function, blood sugar control, and blood pressure regulation. Many magnesium supplements exist, including magnesium oxide, magnesium citrate, magnesium glycinate, and magnesium sulfate.
As I explained in my previous post, “Can You Take Magnesium While Pregnant,” magnesium plays several essential roles in pregnancy and health. Magnesium affects both blood sugar and blood pressure regulation. Research has found that magnesium depletion, especially in the presence of calcium excess, can predispose women to pregnancy complications such as preeclampsia. Women with gestational diabetes are also commonly deficient in magnesium—and gestational diabetes is linked to a higher risk of developing preeclampsia.
Magnesium will not prevent or treat preeclampsia alone, but it does play a role. For both prevention and after diagnosis of preeclampsia, I recommend prioritizing food first. Include plenty of magnesium-rich foods in your diet. Pumpkin seeds, chia seeds, almonds, spinach, avocados, and black beans are a few examples of high-magnesium foods.
Magnesium sulfate therapy has become a standard recommendation by organizations like the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists if there is concern for seizures due to preeclampsia. As early as the 1990s, the MAGPIE trial, a large controlled trial, provided evidence that magnesium sulfate may reduce the risk of eclampsia in women with preeclampsia when compared to other anticonvulsant therapies. An additional controlled study by the Eclampsia Trial Collaborative Group meta-analysis has also demonstrated magnesium sulfate’s effectiveness in reducing the risk of eclampsia.
What Does Magnesium Do For Preeclampsia?
Prevention of Seizures
Magnesium sulfate therapy reduces the risk of seizures associated with preeclampsia and eclampsia by blocking the release of glutamate, which is an excitatory neurotransmitter. When administered through an IV, magnesium raises levels of glutamate in the blood. It crosses the blood-brain barrier to stabilize nerve cell membranes and prevent excessive electrical excitability in the brain. This anti-seizure action can help to reduce the risk of seizures when indicated, as shown in clinical research trials.
Blood Pressure Regulation
Magnesium assists in blood pressure regulation through multiple pathways. It helps dilate and relax blood vessels to improve circulation. It also helps convert angiotensin I to angiotensin II, preventing excess hormone production that can raise blood pressure. Maintaining healthy magnesium levels supports normal blood pressure during pregnancy and may help to limit severe hypertension or preeclampsia.
Nutrient Exchange and Fetal Development
During pregnancy, magnesium contributes to the relaxation of blood vessels, which can enhance blood flow to the placenta. This improved blood flow is crucial for efficiently transferring oxygen and nutrients from the mother’s bloodstream to the developing fetus. As the pregnancy progresses and the demands on the mother’s body increase, maintaining adequate magnesium levels becomes even more critical for ensuring proper circulation and nutrient delivery to support the growing baby’s needs.
Supports Overall Heart and Vascular Health
Magnesium plays a pivotal role in supporting overall heart and vascular health. It helps to keep your blood vessels relaxed and support proper heart rhythm. Consuming plenty of magnesium-rich foods assists in maintaining the integrity and flexibility of blood vessels, potentially reducing the likelihood of hypertension and complications related to preeclampsia.
Gestational Diabetes Management
Studies link low magnesium levels to a higher risk of developing gestational diabetes during pregnancy. Magnesium aids insulin activity and sensitivity, essential for controlling blood sugar levels. While having one doesn’t necessarily guarantee the other, women diagnosed with gestational diabetes may be more likely to be diagnosed with preeclampsia. For those with gestational diabetes, adequate magnesium contributes to better blood sugar management alongside other diet and exercise interventions.

Magnesium Sulfate Therapy For Preeclampsia
Magnesium sulfate may be prescribed to women diagnosed with preeclampsia when complications such as the following are present:
- Severe high blood pressure readings of 160/110 mmHg or higher despite medication to control blood pressure.
- Severe headaches, changes in vision like flashing lights or blurriness.
- Upper abdominal pain under the ribs (can be a sign of liver dysfunction).
- Sudden weight gain of more than 2 pounds in a week due to fluid retention.
- Reduced urine output or dark-colored urine from possible kidney problems.
- Diagnosis of gestational hypertension before 37 weeks of pregnancy.
- Previous history of preeclampsia or existing chronic hypertension.
- Fetal growth restriction was shown on ultrasound.
- Symptoms of preeclampsia along with a high-risk condition like diabetes or renal disease.
- Early onset of symptoms, especially before 34 weeks of pregnancy.
By beginning magnesium sulfate therapy when it is indicated, the chances of experiencing the severe complication of eclampsia (seizures) are significantly reduced.

Magnesium Sulfate Therapy Treatment For Preeclampsia
If you are diagnosed with severe preeclampsia and there are concerns about seizures, your medical team may recommend magnesium sulfate therapy. Here is a breakdown of what to expect with the treatment process (This is an example. The timing, process, or dosage in your situation may be different.):
Admission to the Hospital: You will likely be admitted for observation and to begin IV magnesium sulfate therapy. Various monitors will be placed to track vital signs.
Loading Dose: An initial high “loading dose” of 4-6 grams of magnesium sulfate (for example, this may vary) will be diluted and rapidly administered intravenously over 20-30 minutes. This quickly increases magnesium levels in your blood.
Maintenance Infusion: After the loading dose, a continuous infusion of 1-2 grams of magnesium per hour will be administered via an IV pump. This keeps therapeutic levels stable to prevent seizures.
Monitoring Period: You will likely be closely monitored for at least 24 hours after starting the infusion. Expect frequent blood pressure checks, urine output monitoring, and reflex/breathing assessments by nurses. Blood tests every 4-6 hours will check magnesium levels in your body.
Magnesium Level Adjustment: Depending on side effects and magnesium levels in tests, the infusion rate may need slight adjustment up or down by your medical team to balance benefits and risks.
Duration of Treatment: Most women receive magnesium sulfate for 24 hours after symptoms improve.
Gradual weaning: When treatment is complete, the magnesium infusion will gradually be weaned over 2-4 hours to avoid the potential side effects of ending it abruptly.
Support after Treatment: Even after magnesium therapy ends, you will likely remain under close observation in the hospital, depending on your preeclampsia severity and pregnancy progress.
Possible Side Effects of Magnesium Sulfate Therapy
- Flushed skin or sweating: Due to magnesium’s role as a calcium channel blocker, flushing or sweating may occur as blood vessels dilate. This is usually mild.
- Muscle weakness: At high levels, magnesium could cause decreased deep tendon reflexes and lethargy. This poses little risk with careful IV monitoring.
- Nausea or vomiting: Rarely, magnesium administration may provoke nausea or vomiting in some women. For healthy snacks to help with nausea during pregnancy, check HERE.
- Low blood pressure: In severe preeclampsia, magnesium therapy alongside other antihypertensive drugs could potentially cause transient low blood pressure. No action is usually needed.
- Respiratory issues: At toxic doses, magnesium could slow breathing rate. However, risks are very low under medical supervision for recommended treatment durations.
- Burning at IV site: Infusion into veins rarely triggers local pain, redness, or swelling. Switching IV access sites prevents complications.
- Fetal bradycardia: In rare cases, high magnesium levels may temporarily cause fetal heart rate abnormalities, posing no lasting risks.
Magnesium sulfate’s benefits far outweigh potential side effects when managed closely by medical staff. Serious problems are uncommon when monitoring occurs, and treatment protocols are correctly followed. Consult with and follow the guidance of your medical team.

Consuming adequate magnesium can help support blood pressure regulation during pregnancy.
Preeclampsia can be an overwhelming diagnosis to receive. Fortunately, several lifestyle and nutrition interventions can help to support the prevention and management of preeclampsia during pregnancy. Magnesium is an essential nutrient that plays a role in hundreds of processes in the body. It also plays a role in blood pressure control.
In summary, incorporating plenty of magnesium-rich foods benefits all pregnant women. Magnesium supplementation may be warranted for some individuals. Magnesium sulfate therapy is commonly prescribed for preventing seizures associated with severe preeclampsia and eclampsia. When administered properly according to guidelines under medical supervision, it can provide meaningful benefits for both mothers and babies at risk for seizures due to preeclampsia.
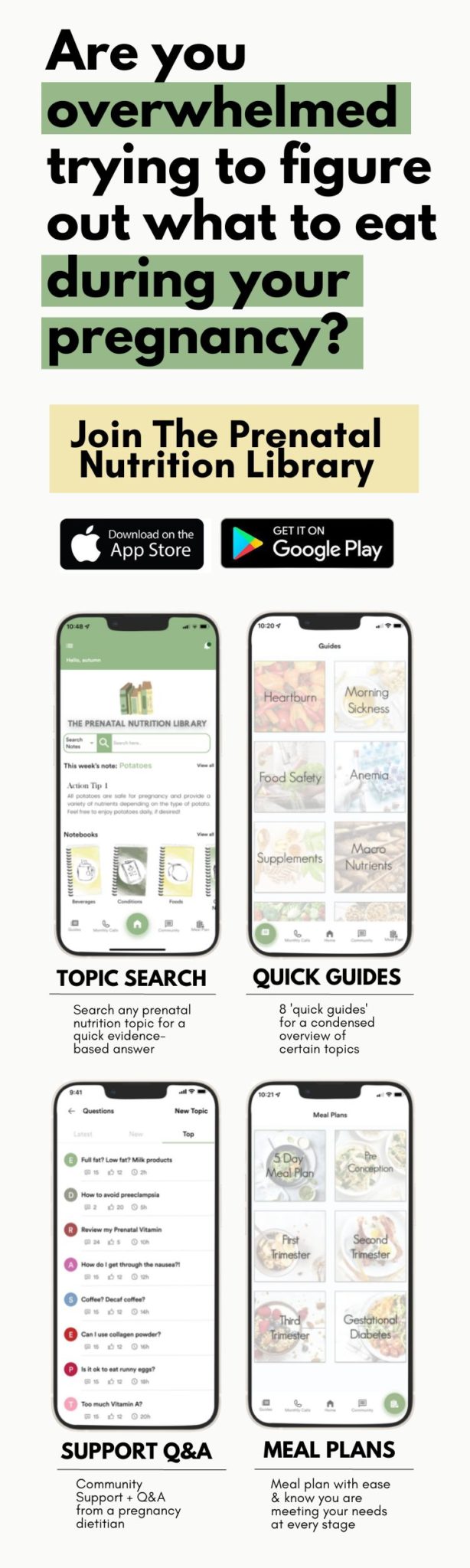
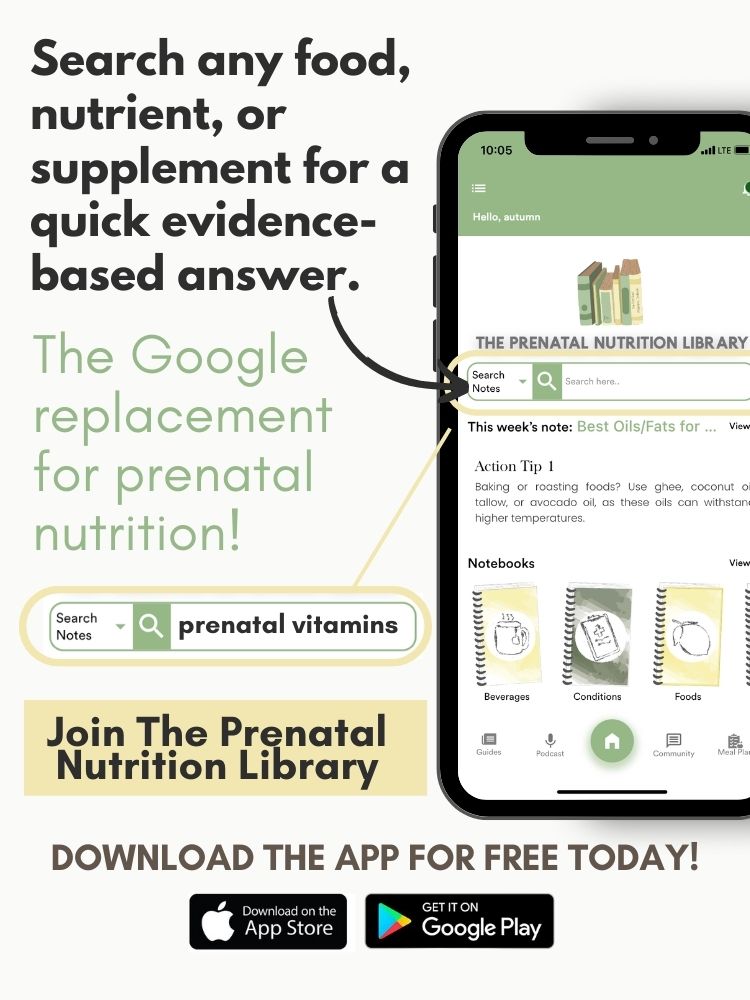
For more valuable information on nutrition during all stages of your pregnancy journey, sign up for The Prenatal Nutrition Library. When you sign up, you can search thousands of nutrients, foods, supplements, labs, and more for a quick, evidence-based answer right at your fingertips with our easily searchable app. Download the app for FREE on Apple or Android to peek inside and get a FREE 1-week meal plan!